Search Results
Results for: 'oxidation-reduction reactions'
Types of energy transfer reactions: oxidation-reduction reactions and ATP generation reactions
By: HWC, Views: 11578
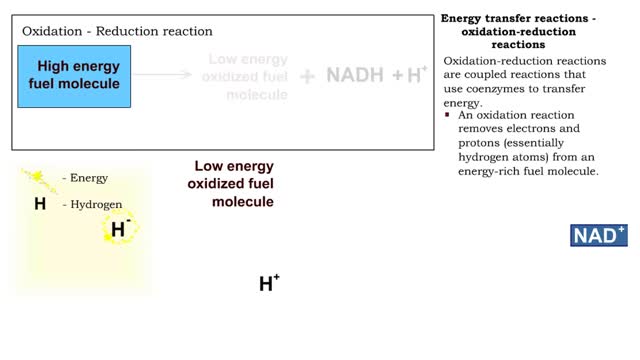
■ Metabolism balances anabolic and catabolic reactions. ■ Anabolism is energy transfer from ATP to simpler molecules in order to build them up into larger, more complex molecules. ■ Catabolism is breaking down larger, more complex molecules, usually to transfer energy from them in order...
By: HWC, Views: 11286
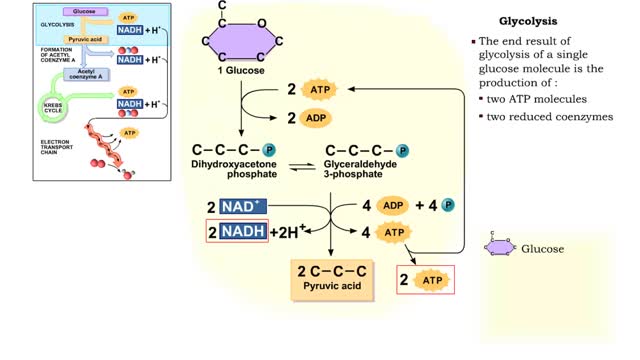
The first reactions involve a single 6-carbon glucose sugar undergoing phosphorylation using two ATP molecules and resulting in two 3-carbon compounds. • The rest of this pathway involves an oxidation reduction reaction, forming two reduced coenzymes, and generation of four ATP molecules. ...
Splitting of Sugar, Oxidation/ Reduction & ATP Generation
By: HWC, Views: 10695
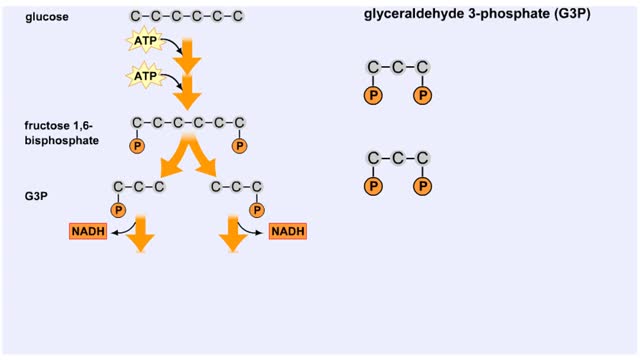
The next reaction shows us the meaning of "glycolysis" or the splitting of glucose. The fructose bisphosphate molecule is split into two molecules each containing 3 carbons as the backbone. FBP is split into two 3-carbon molecules called G3P, or glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. Notice that the phos...
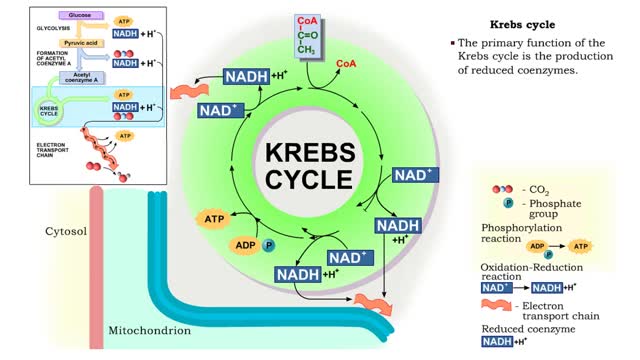
Krebs cycle : Formation of acetyl coenzyme A and Electron transport chain
By: HWC, Views: 11153
The oxidation of glucose to produce ATP is cellular respiration. Four sets of reactions are involved: Glycolysis Formation of acetyl coenzyme A Krebs cycle reactions Electron transport chain reactions • The second pathway of glucose catabolism, formation of acetyl coenzyme A, is a transi...
Lipid catabolism - lipolysis and beta oxidation and oxidation of fatty acids
By: HWC, Views: 11280
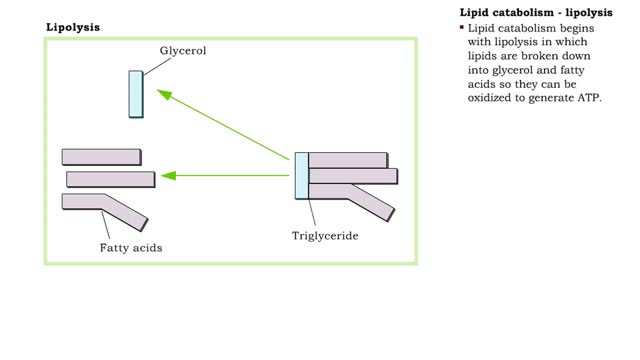
• Digestion hydrolyzes lipids into fatty acids and glycerol. • Fatty acids and glycerol are: • Oxidized to generate ATP. • Used to produce triglycerides that are stored as energy reserves in adipose tissue. • Lipid catabolism begins with lipolysis in which lipids are broken do...
Fermentation - When Oxygen Is Absent, Pyruvate to Lactate & Pyruvate to Ethanol
By: HWC, Views: 10416
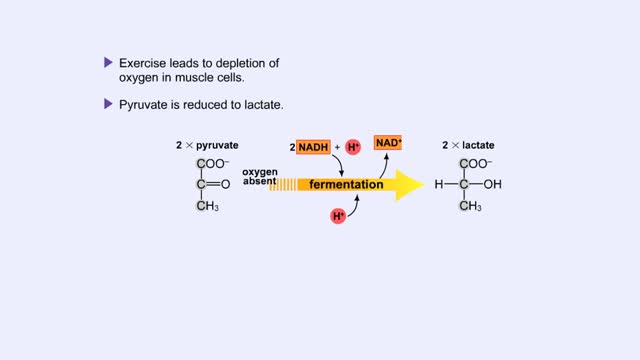
Pyruvate is the end product of glycolysis. If oxygen is present, pyruvate enters the mitochondrion where further energy yielding reactions of the Krebs cycle will take place. However, if oxygen is not present, pyruvate will enter a pathway called fermentation. This pathway regenerates NAD+ fro...
Photosynthesis overview Animation
By: HWC, Views: 5054
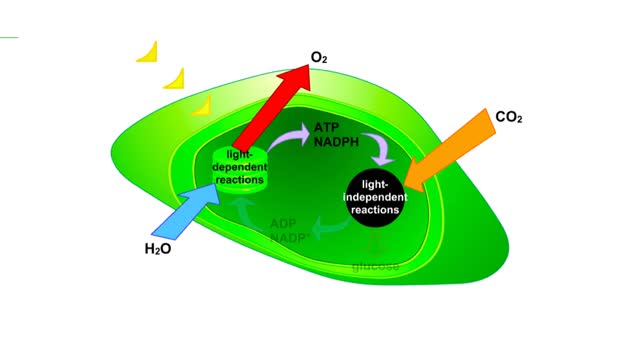
Illustration of the interrelationships of the light-dependent and light-independent reactions of photosynthesis. The light-dependent reactions split water, and produce ATP and NADPH. Oxygen is a by-product of these reactions. ATP and NADPH, together with carbon dioxide, are reactants in ...
By: Administrator, Views: 13805
Atrophy is the partial or complete wasting away of a part of the body. Causes of atrophy include mutations (which can destroy the gene to build up the organ), poor nourishment, poor circulation, loss of hormonal support, loss of nerve supply to the target organ, excessive amount of apoptosis of c...
Digestive chemicals - types & enzymes
By: HWC, Views: 10970
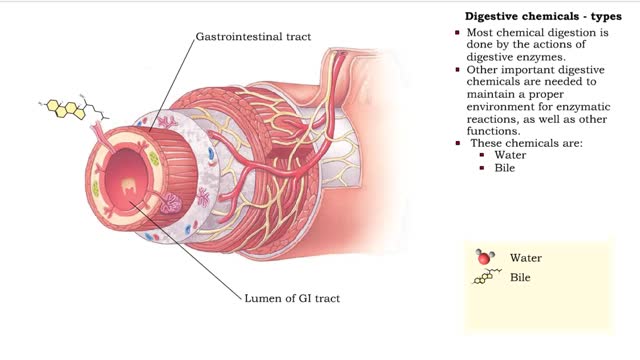
• Chemical digestion breaks down food as it moves through the digestive tract. • Using enzymes and other digestive chemicals, the process reduces food particles into nutrient molecules that can be absorbed. • Most chemical digestion is done by the actions of digestive enzymes. • O...
Advertisement